前言
昨天我們已經結束了 stack 相關的內容,今天要開始介紹 PWN 中另一個非常重要的部分:Heap。相較於 stack,heap 涉及更多基礎知識,是一個需要深入了解的重要環節。
What is Heap?
在程式執行過程中,為了更有效率地分配記憶體空間,會使用動態記憶體配置(Dynamic Memory Allocation)。不同的使用場景會使用不同的記憶體分配器,例如:glibc 使用的 ptmalloc、firefox 的 jemalloc 以及 chrome 的 tcmalloc。而我們所說的 heap,就是這些分配器取得的一塊連續的虛擬記憶體空間。我們接下來的討論主要集中在 glibc 所使用的記憶體分配器上。
malloc
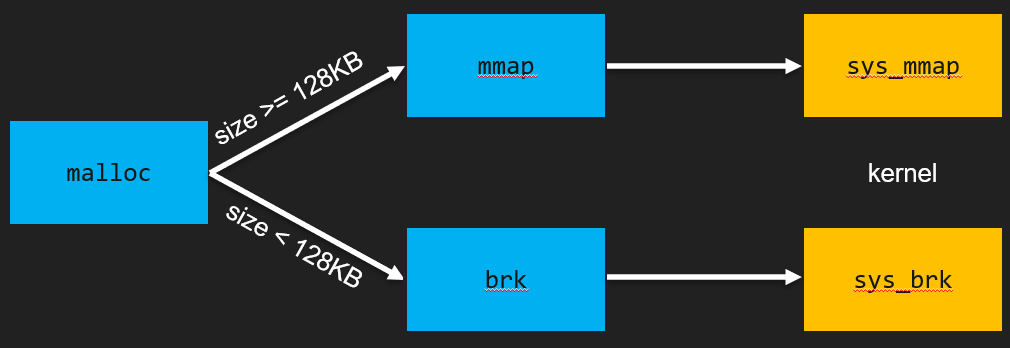
malloc 是用來分配記憶體的函數,基本原則是需要多少分配多少。這樣可以提升程式的記憶體分配效率,避免不必要的空間浪費。其實,malloc 的運作過程相當複雜,但若簡單整理,可以理解為:如果分配的 size $<$ 128KB,系統會呼叫 brk 來進行配置;相反,若 size $\ge$ 128KB,則會使用 mmap 進行分配。
main arena
雖然如果分配的 size 小於 128KB 會通過 brk 來向 kernel 申請空間,但實際上並不只分配請求的空間,系統會直接給予 132KB 的 heap 段,這段記憶體被稱為 main arena。
以下是 GLIBC 2.35 關於 struct malloc_state 的程式碼:
1struct malloc_state
2{
3 /* Serialize access. */
4 __libc_lock_define (, mutex);
5
6 /* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
7 int flags;
8
9 /* Set if the fastbin chunks contain recently inserted free blocks. */
10 /* Note this is a bool but not all targets support atomics on booleans. */
11 int have_fastchunks;
12
13 /* Fastbins */
14 mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
15
16 /* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
17 mchunkptr top;
18
19 /* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
20 mchunkptr last_remainder;
21
22 /* Normal bins packed as described above */
23 mchunkptr [NBINS * 2 - 2];
24
25 /* Bitmap of bins */
26 unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
27
28 /* Linked list */
29 struct malloc_state *next;
30
31 /* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
32 by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
33 struct malloc_state *next_free;
34
35 /* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
36 the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
37 free_list_lock in arena.c. */
38 INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
39
40 /* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
41 INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
42 INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
43};
可以看到這裡有 flag、last_remainder、fastbin 和 bins 等欄位,這些名詞將在後續內容中詳細說明。
second or more malloc
當程式在第二次或後續的 malloc 操作時,只要總共分配出去的空間小於 128KB,程式不會再向 kernel 申請額外空間。只有當分配總量超過 128KB 時,程式才會再次使用 brk 向 kernel 申請空間。另外,GLIBC 也提供了將記憶體釋放回系統的函數 free()。但需要注意的是,雖然記憶體空間被 free 掉,但從 main arena 分配出去的空間並不會馬上歸還給 kernel,而是交回給 glibc 進行管理。
總結
以上是關於 heap 和 malloc 的簡單介紹。實際上,heap 還涉及許多名詞與概念,如 chunk 和 bin,這些將會與記憶體分配與釋放機制相關聯。在接下來的內容中,我們會更深入地探討這些細節。